Full country name
Federal Republic of Germany
Government type: Federal Republic.
Germany is a modern and stable democracy. Tourist facilities are highly developed. In larger towns, many people can communicate in English.
More: Germany Government Structure and Political System / States
Nationality
German(s) (noun) German (adjective)
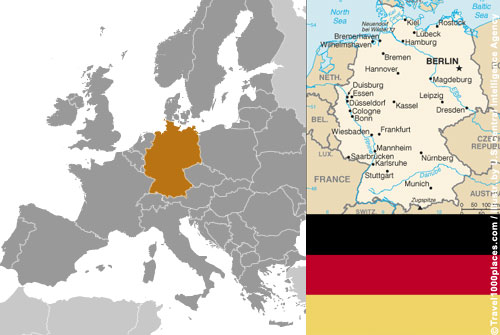
German Flag
Three equal horizontal bands of black (top), red, and gold; these colors have played an important role in German history and can be traced back to the medieval banner of the Holy Roman Emperor – a black eagle with red claws and beak on a gold field.
Ethnic groups:
German 91.5%, Turkish 2.4%, other 6.1% (made up largely of Greek, Italian, Polish, Russian, Serbo-Croatian, Spanish)
Religions
Protestant 34%, Roman Catholic 34%, Muslim 3.7%, unaffiliated or other 28.3%
Languages
German (official language)
The education system offers as 2nd language predominantly: English, French, Latin
National Anthem Lyrics: Deutschlandlied
The lyrics are taken from the 3rd verse (strophe) of the poem “Das Lied der Deutschen”, created by August Heinrich Hoffmann von Fallersleben on the German island of Helgoland in the year 1841.
The melody is taken from the “Kaiserlied” composed by Joseph Haydn in Vienna (Austria) in 1796/97.
“Einigkeit und Recht und Freiheit
Für das deutsche Vaterland!
Danach lasst uns alle streben,
Brüderlich mit Herz und Hand!
Einigkeit und Recht und Freiheit
Sind des Glückes Unterpfand:
Blüh im Glanze dieses Glückes,
Blühe, deutsches Vaterland!”
German National Anthem played by the Stabsmusikkorps of the Bundeswehr (Bundeswehr is the German Military)
Political, economical, and historical summary
As Europe’s largest economy and second most populous nation (after Russia), Germany is a key member of the continent’s economic, political, and defense organizations.
European power struggles immersed Germany in two devastating World Wars in the first half of the 20th century and left the country occupied by the victorious Allied powers of the US, UK, France, and the Soviet Union in 1945.
With the advent of the Cold War, two German states were formed in 1949: the western Federal Republic of Germany (FRG) and the eastern German Democratic Republic (GDR). The democratic FRG embedded itself in key Western economic and security organizations, the EC, which became the EU, and NATO, while the Communist GDR was on the front line of the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact.
The decline of the USSR and the end of the Cold War allowed for German unification in 1990. Since then, Germany has expended considerable funds to bring Eastern productivity and wages up to Western standards.
In January 1999, Germany and 10 other EU countries introduced a common European exchange currency, the euro.
Population and Largest Cities
Total population: 82,329,758 (July 2009 est.).
Next census: 2011
(Capital) Berlin (~3.41 million), Hamburg (~1.77 million), Munich (~1.31 million), Cologne (~995 000), Frankfurt (~644 000), Essen (~582 000), Dortmund (~586 000), Stuttgart (~597 000), Dusseldorf (~581 000), Bremen (~547 000), Hannover (~518 000).
Geography
Germany is located in Central Europe, bordered by 9 other countries. It has a coastline of 2,389 km (1 484 mi) and borders the Baltic Sea (in German ‘Ostsee’) and the North Sea (in German ‘Nordsee’).
Germany’s land borderline is 3,621 km (2 250 mi) long and the border countries are:
Austria 784 km (487 mi), Belgium 167 km (103 mi), Czech Republic 646 km (401 mi), Denmark 68 km (42 mi), France 451 km (280 mi), Luxembourg 138 km (85 mi), Netherlands 577 km (358 mi), Poland 456 km (283 mi), Switzerland 334 km (207 mi).
Germany’s total land area is: 348,672 sq km (134 627 mi). The water area is: 8,350 sq km (3 224 mi); in total 357,022 sq km (137 851 mi)
Germany is slightly smaller than Montana, USA.
Economy Germany
Summary
The German economy – the fifth largest economy in the world in PPP terms and Europe’s largest – is a leading exporter of machinery, vehicles, chemicals, and household equipment and benefits from a highly skilled labor force.
Like its western European neighbors, Germany faces significant demographic challenges to sustained long-term growth. Low fertility rates and declining net immigration are increasing pressure on the country’s social welfare system and necessitate structural reforms.
The modernization and integration of the eastern German economy – where unemployment can exceed 20% in some municipalities – continues to be a costly long-term process, with annual transfers from west to east amounting in 2008 alone to roughly $12 billion.
Reforms launched by the government of Chancellor Gerhard SCHROEDER (1998-2005), deemed necessary to address chronically high unemployment and low average growth, contributed to strong growth in 2006 and 2007 and falling unemployment, which in 2008 reached a new post-reunification low of 7.8%.
These advances, as well as a government subsidized, reduced working hour scheme, have helped to explain the relatively modest increase in unemployment during Germany’s 2008-09 recession – the deepest since World War II. GDP grew just over 1% in 2008 and contracted roughly 5% in 2009. Germany crept out of recession in the second and third quarters of 2009, thanks largely to rebounding manufacturing orders and exports – primarily outside the Euro Zone – and relatively steady consumer demand.
The Germany economy probably will recover to about 1.5% growth for the year 2010. However, the relatively strong euro, tighter credit markets, and an anticipated bump in unemployment could cloud Germany’s medium-term recovery prospects.
Stimulus and stabilization efforts initiated in 2008 and 2009 and tax cuts introduced in Chancellor Angela MERKEL’s second term will increase Germany’s record budget deficit, which is expected to exceed 5% of GDP in 2010.
The EU has given Germany until 2013 to get its consolidated budget deficit below 3% of GDP.
A new constitutional amendment likewise limits the federal government to structural deficits of no more than 0.35% of GDP per annum as of 2016.
Industries
Among the world’s largest and most technologically advanced producers of iron, steel, coal, cement, chemicals, machinery, vehicles, machine tools, electronics, food and beverages, shipbuilding, textiles.
Transportation Germany
Airports
ca. 550
Airports – with paved runways:
total: 330
over 3,047 m: 13
2,438 to 3,047 m: 52
1,524 to 2,437 m: 58
914 to 1,523 m: 72
under 914 m: 135 (2009)
Airports – with unpaved runways:
total: 220
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 33
under 914 m: 184 (2009)
Heliports
ca. 25
Pipelines
gas 24,364 km; oil 3,379 km; refined products 3,843 km (2009)
Railways
total: 41,896 km
Country comparison to the world: 6
Standard gauge: 41,641 km 1.435-m gauge (20,053 km electrified)
Narrow gauge: 75 km 1.000-m gauge (75 km electrified); 24 km 0.750-m gauge (24 km electrified)
Roadways
total: 644,480 km
Country comparison to the world: 11
Paved: 644,480 km (includes 12,600 km of expressways)
Note: includes local roads
Waterways
7,467 km
Country comparison to the world: 19
Note: Rhine River carries most goods; Main-Danube Canal links North Sea and Black Sea
Merchant marine
total: 393
country comparison to the world: 26
By type: bulk carrier 2, cargo 43, chemical tanker 13, container 284, liquefied gas 5, passenger 5, passenger/cargo 27, petroleum tanker 11, roll on/roll off 3
Foreign-owned: 11 (China 2, Cyprus 2, Denmark 1, Finland 4, Netherlands 1, Sweden 1)
Registered in other countries: 2,998 (Antigua and Barbuda 941, Australia 2, Bahamas 44, Bermuda 22, Brazil 6, Bulgaria 63, Burma 1, Canada 3, Cayman Islands 15, Cyprus 189, Denmark 9, Denmark 1, Estonia 1, Finland 1, France 1, Georgia 2, Gibraltar 129, Hong Kong 6, India 2, Indonesia 1, Isle of Man 56, Jamaica 4, Liberia 849, Luxembourg 5, Malaysia 1, Malta 91, Marshall Islands 235, Mongolia 4, Morocco 2, Netherlands 75, Netherlands Antilles 43, Norway 1, NZ 1, Panama 44, Portugal 20, Russia 1, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines 3, Singapore 24, Slovakia 3, Spain 5, Sri Lanka 5, Sweden 5, Turkey 1, UK 76, US 5)
Ports and terminals
Bremen, Bremerhaven, Duisburg, Hamburg, Karlsruhe, Lubeck, Rostock, Wilhemshaven

